
You just need to add a flag to the `ls` command that will ask it to show hidden folders, and that’s the `-laf` flag. With a bit of magic, though, we can see it ourselves. git stores the metadata and object database for the. git, your project is a local project and not a git project, that means you cannot perform any git operations. That period in front of the `.git` folder means that it’s actually a hidden folder, so it won’t show up in your Finder or Explorer window and is typically only meant for scripts and OS-level commands to access. git folder is the directory which is created when you do git init (in case of a new project) or you do git clone (in case of pulling a project from somewhere else). If `ls` and seeing your project’s folders isn’t enough for you, there’s another technique to be even more sure that you’re in the right place. The other way is to initialize a new Git repository using the `git init` command to set up version tracking in a new folder.Įither way, that `.git` folder I mentioned should exist in the repository’s root (top-most folder). It then copies the data from the existing repository.

Internally, git clone first calls git init to create a new repository. You can always rename your target dir or move it around as you wish (one level up for example) - git does not really care, as long as.
 git subdirectory to the current directory and makes it possible to start recording revisions of the project. git clone
git subdirectory to the current directory and makes it possible to start recording revisions of the project. git clone I want to check this directory into git in place. Transform the current directory into a Git repository.
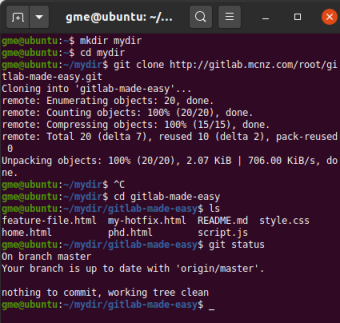
One way is to run the `git clone` command and clone a repository from an existing repository (whether that repository exists locally on your computer or on a server running Git such as ). I have a non-empty directory (eg /etc/something) with files that cannot be renamed, moved, or deleted. Generally speaking, you can get a Git repository locally in one of two ways.
#Git clone into current directory how to
How to really know you’re in a Git repository


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
